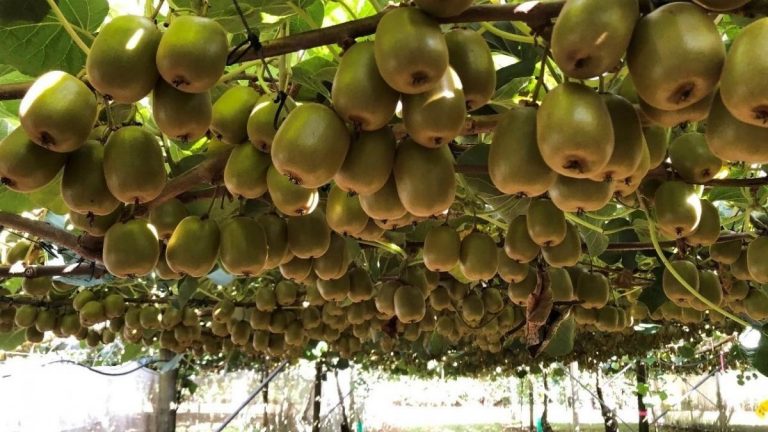
Kiwi grows in most temperate regions. This fruit is commercially cultivated in sturdy structures, usually equipped with an irrigation system that, besides watering, prevents spring frost damage. It is advisable to avoid planting in high-altitude areas due to colder winters and the risk of spring frosts. The plant’s mortality rate is particularly high during the first two years after planting, as untimely or excessive frost can burn and blacken its buds. However, there is no need to worry as the plant will sprout again from the main trunk in the near future.
Where can you plant kiwi trees?

In Iran, the regions that meet all the climatic conditions for growing this tree are primarily Mazandaran province, followed by Gilan province. Depending on soil fertility and quality, this plant can spread up to a four-meter radius. Therefore, it is appropriate to install a wire trellis and train the vine on it. A trellis with three wires at 70 cm, 140 cm, and 200 cm lengths is sufficient, and young branches should be tied to the trellis.

Kiwi grows best in deep alluvial soils. It thrives better in loamy and silty-loam soils than in sandy-loam soils. The ideal soil for cultivating this plant should be light, rich in organic matter, well-drained, and sufficiently deep. Due to its sensitivity to salinity, especially boron and sodium salts, irrigation water should have minimal salinity. Chloride, bicarbonate, boron, and sodium cause the most damage to this plant. The optimal pH for kiwi growth is between 5.5 and 6.5. About 1500 mm of rain per year, well-distributed, is sufficient to meet its water needs. In regions with hot summers up to 45°C, kiwi can be grown if adequately irrigated (74-93 cubic meters per hectare per day). At 32°C in summer, it needs 55 cubic meters of water per hectare per day.
Where can you plant kiwi trees?
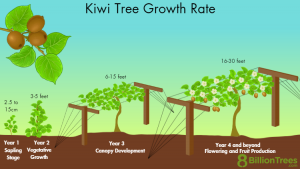
The best time to plant kiwi is in September and October (ideal time) or March and April. The soil is crucial for the kiwi’s root expansion, so it must be considered to achieve the best composition. The best soil for kiwi cultivation is humus-rich sandy soil. This mixture, which consists of light sandy soil (50% well-rotted manure and 50% sea sand), is the most suitable combination. Before planting, plow the main field, then use a rotary tiller or disc harrow. If the soil is light, dig holes 120 to 150 cm in diameter and 50 cm deep, mix the excavated soil with 50% manure and some humus or leaf mold, then refill the hole to 40 cm above the ground level, making the mound surface flat. If the soil is semi-heavy, dig holes 120×150 cm, mix the excavated soil with 50% sand and manure, refill the hole to 70 cm above ground level, flatten the mound surface, and plant the seedling. If the land has heavy soil, installing drainage between the kiwi rows is necessary.
Kiwi plants are usually dioecious, meaning each plant is either male or female. Only female plants bear fruit, and that too only when pollinated by a male plant. One male pollinator is needed for three to eight female vines. Pollination is carried out by wind and insects, with honeybees being particularly important for pollinating kiwi flowers.
Male flowers open earlier than female ones, which is one way to identify male plants. Kiwi flowers are white and eventually turn golden yellow. They do not produce nectar but emit a pleasant fragrance. However, due to the lack of nectar, they are not attractive to bees, making kiwi pollination challenging. Some producers apply collected pollen to female flowers manually. The most successful pollination method is saturation pollination, which involves placing many beehives in the orchards, forcing bees to use the kiwi flowers due to intense competition.







